Search engines and Search Queries
SEO – Search engine optimization is an important part of digital marketing strategy. It brings organic traffic from search engines to the websites.
Google still remains the No.1 search engine with the global market share over 89%. These statistics are from SEMRUSH. We will use Google as an example for search engine in the entire context.
Google’s mission is to bring world’s information together and make it accessible and useful. Google’s index act as a huge repository that can store vast amount of data. When people use google search, they type the question with an intent. It is called the ‘search query’ and also determined as a keyword in SEO terminology.
Search engines match these keywords with the data in its index, and pulls out the most relevant information to display in search results. This is how people receive information for their search queries.
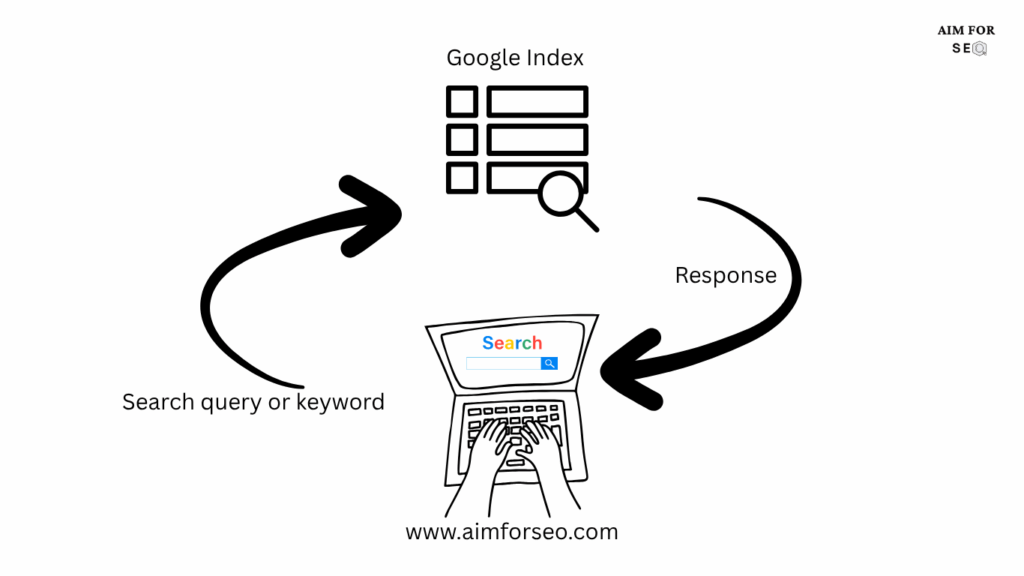
Search engines use ‘spiders’ also known as ‘crawlers’ to do this task.
Bots = Spiders = Crawlers.
Webmasters and Web spiders
As mentioned earlier, Google’s index store a lot of information across the world. But how does it get this information (data)?
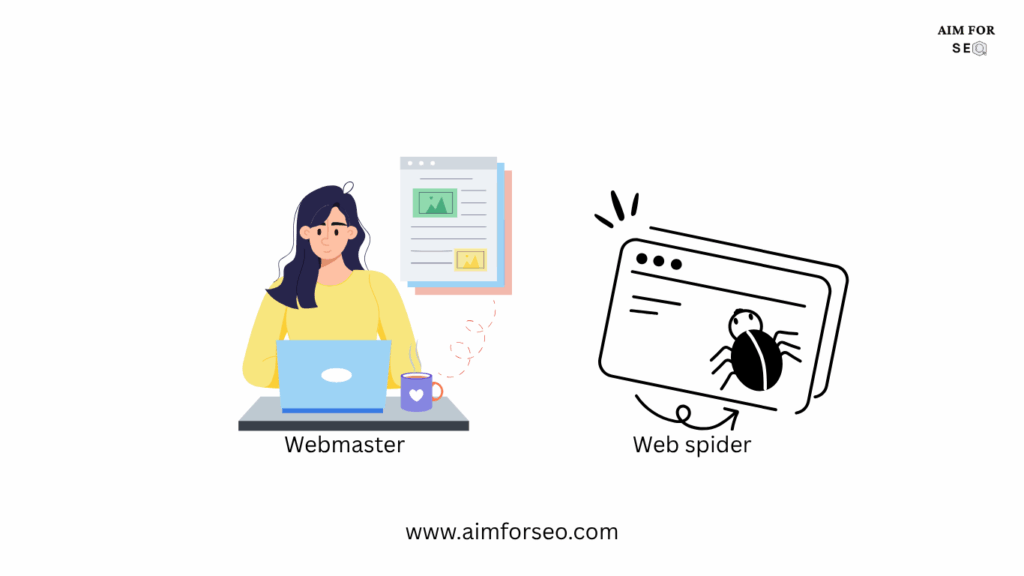
Search engines get this information from websites and blogs that are written by webmasters and content writers.
Google spiders find these website links on the internet.
They follow these links and crawl the entire website. They crawl each and every page and store the information in its index.
Indexing and Information
Not all webpages on the internet are available to search engines.
Webmaster’s can choose whether their web pages should be indexed by search engines or not.
They can instruct Google crawlers not to index their webpages by using a ‘noindex’ meta tag in HTML or HTTP header.
HTML Tag – Within the page, we tell crawlers not to index this page.
HTTP Header – in the server response, we tell crawlers not to index the page even before they read its content.
Some webpages doesn’t necessarily have to be available for everyone.
Example – a thank you page, login page and FAQs, terms and conditions etc.
Therefore, one can control what information gets indexed and what doesn’t.
The next chapter covers the most important basics of seo for a good start.
Read all chapters of Beginner’s SEO Guide from here.


